Improving security, efficiency, and convenience, while reducing risk and fraud.
International air travel is expected to reach 1.8B arrivals per year by 2030.
Introduction
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, international air travel was expected to grow to 1.8B arrivals per year
by 20301. While the pandemic has undoubtedly caused an unprecedented short-term shock to the industry, growth over the long-term is still likely to occur, albeit potentially in different ways.
The pandemic has not only raised obvious health considerations that must be accounted for as part of cross-border security, but governments, airports, and airlines must also consider how air travel will need to adapt to broader demographic shifts and the strain they will place on existing travel infrastructures.
Within the next decade, much of the global population will comprise of post-digital generations; those who have engaged with online technology since childhood, and actively leverage it in various ways to manage their lives. Airports and airlines will primarily be tasked with undergoing a digital transformation to improve the passenger experience for digital natives, while reducing costs. Governments, in turn, will need to adopt reliable technologies to facilitate legitimate border crossings, while identifying unlawful movements and reducing the spread of harmful pathogens.
Among the significant technology-led trends shaping the future of air travel, Digital ID enables a low-touch airport experience, improves security oversight, accelerates passenger processing and reduces resources required to manage the journey of these post-digital travellers.
How is air travel evolving?
Post-digital travellers expect a more personalized level of service and less friction points along their journey. Digital ID leverages advances in emergent technologies such as biometrics (to securely verify travellers), distributed ledgers (to create a trusted network), and cryptography (to simultaneously advance the security capabilities) on which governments rely, while standardizing and improving the traveller’s end-to-end experience along their journey.

How does digital ID help?
Governments
- Strengthens security, by shifting subjective identity and clearance steps into an automated and reliable authentication process.
- Minimizes costs, by reducing staffing requirements due to efficiencies gained from automated scanning and verification technologies.
Airlines
- Reduces fraud, by leveraging additional authentication, to prevent illegitimate chargebacks on legitimate purchases and exploitation of frequent flyer programs.
- Enables increased capacity and efficiency, by eliminating time-consuming, manual identification checkpoints and facilitating faster clearance for both inbound and outbound passengers.
Passengers
- Improves privacy and security, giving passengers control and transparency of the information they share.
- Offers greater convenience and reduces risk, allowing travellers to use their devices throughout their journey, moving seamlessly through each checkpoint with a tap while reducing the risk of pathogen transmission.
User Journey
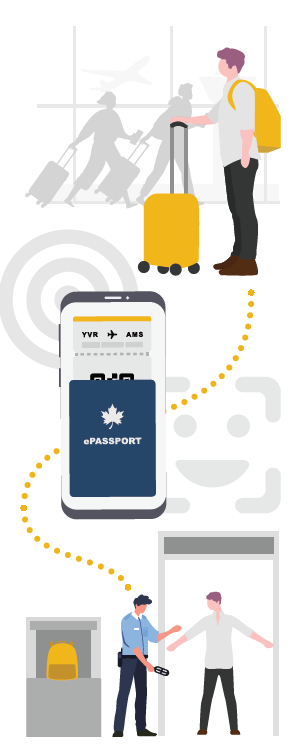
Step 1: Open Digital Wallet
Julian arrives at the airport, checks his bags, and proceeds to the security checkpoint. He opens his digital wallet, preparing his Digital Travel Credentials for verification.
Step 2: Tap or Scan Device
The security agent points out the terminal where Julian must tap his device to share the necessary information from his DTC and verify his identity.
Step 3: Authentication & Verification
Upon authenticating, Julian is prompted to share his information and perform a liveliness detection test. The terminal flashes green once he taps his device and has been verified.
Step 4: Proceed
Upon verification, this credential exchange is logged in Julian’s digital wallet and he proceeds onward.
Digital Travel Credential (DTC)
The Digital Travel Credential (DTC) is a secure, mobile, verifiable, and unique biometric token, which contains a traveller’s facial image, personal details, and security features to support its authentication. In the medium to long term, the DTC will enable governments to have far greater trust in biometric and biographic data they receive directly from passengers as it will instantly confirm that the data is authentic, isn’t counterfeit and hasn’t been tampered with in any way.

Our Principles
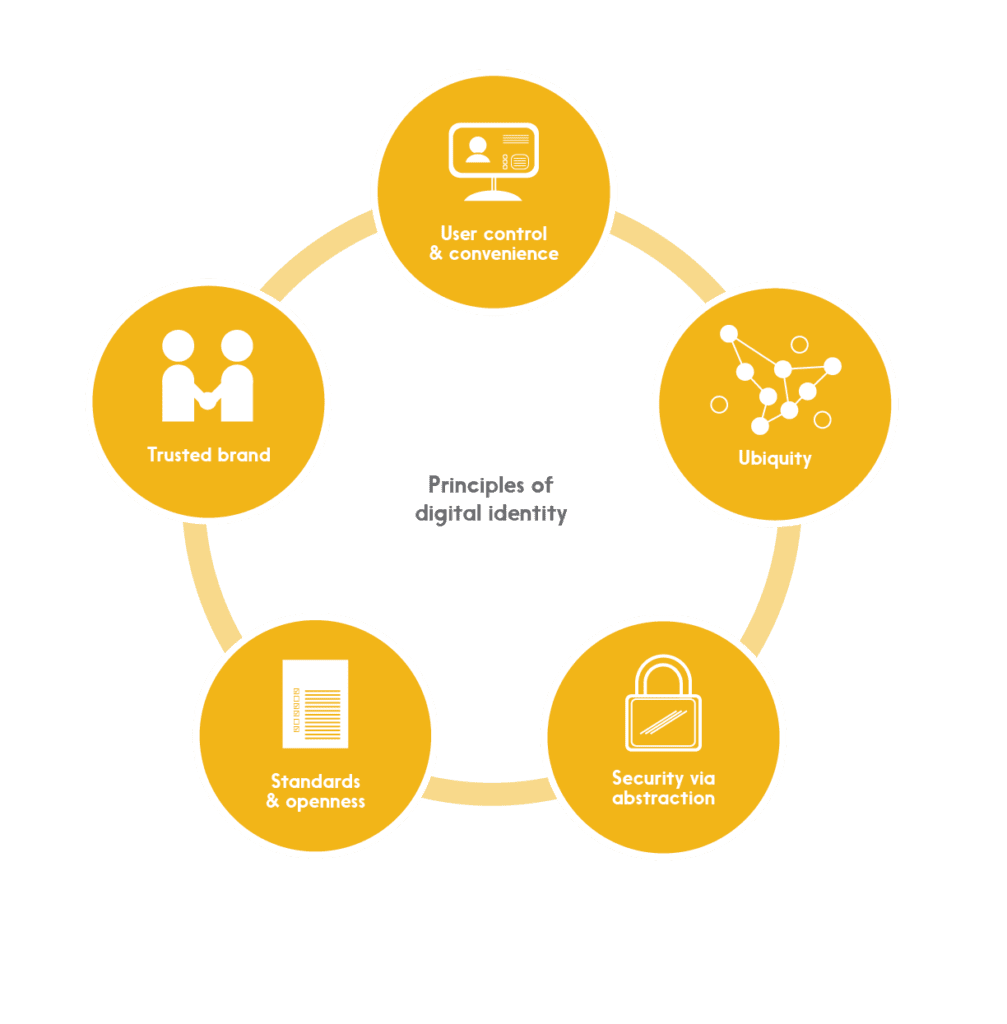
Digital identity is easy to theorize about, but architecting and implementing a comprehensive, secure, and sustainable system is another matter entirely – and an important part of getting it right is having a clearly articulated set of principles to guide the effort. We believe that there are five:
User Control & Convenience
No one wants to entrust a system with their personal details if those details are going to be transferred to and stored by numerous parties – especially if this happens without the user’s knowledge and express consent. While ensuring user control, an identity system must also be convenient and easy; if it isn’t, it won’t be adopted by users, many of whom are already used to intuitive apps on mobile devices.
Standards & Openness
In any dynamic system, it’s difficult to predict what the future will look like – so it’s important to build today’s solutions on universally-agreed standards. Not only does this reduce costs by eliminating the expense of building and then later having to adapt custom, one-off solutions, but it enables solutions built by others in the future to “plug into” the initial solution. Openness encourages adoption, innovation, and flexibility.
Ubiquity
Security risks abound when people create different identities and passwords for each public and private service they access. They’ll often default to a single, easy-to-remember (and easy to crack) password, for example. At the same time, a digital identity that only applies to a handful of services will probably not be well- adopted. A ubiquitous system is a more convenient and a more secure system.
Trusted Brand
No user is likely to adopt an identity solution built or maintained by an organization they don’t trust. The question of identity is simply too important, and the impact of identity theft too great, to leave this to chance. Further, building a large-scale (and ubiquitous) solution will require the cooperation and coordination of many players, and these players need to trust each other and the organization leading the effort.
Security via Abstraction
Even with the best user controls, a certain amount of identity data must be part of transactions in any given ecosystem. A highly effective way of securing that data is to “abstract” it, by replacing a private identifier with a publicly available one (like a person’s email address) or by replacing it with a randomized number that serves as an authorized “token” for the purposes of the transaction – and is not useful for any other purpose.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic will undoubtedly continue to deter air travel in the near future, but travellers will flock to new destinations in greater numbers over the next decade. Governments and airlines will rely on emergent technologies to improve the capacity and efficiency at airports while also providing a safe and seamless experience the post-digital traveller will come to expect.
The labour-intensive approval process where travellers queue to prove who they are by presenting travel documents is coming to an end. Digital ID offers numerous benefits and advantages over these traditional processes, enabling a low-touch airport experience, while providing a highly secure, fraud-resistant, and convenient means of traveller authentication along the numerous checkpoints in their journey.
If you’re interested in collaborating with Interac on the future of Digital ID, drop us a line at
digitalid@interac.ca
Post-digital travellers expect a more personalized level of service and less friction points along their journey.
1 World Tourism Barometer – UNWTO (January 2017)



